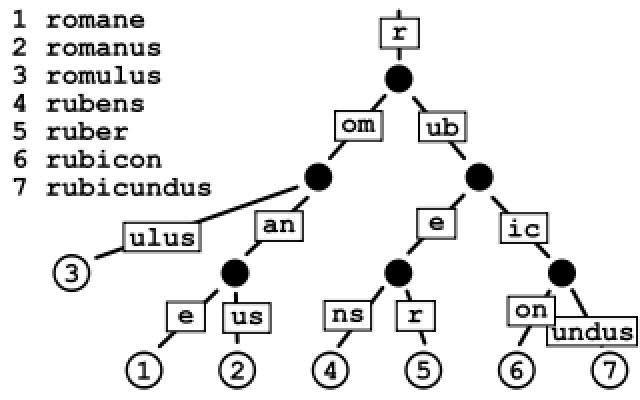
| Application | http | user-level daemon |
| Presentation | ||
| Session | ||
| Transport | TCP | kernel (user |
| Network | IP | kernel |
| Link | Ethernet (frames) | Hardware/firmware/device driver; uses software-maintained addresses |
| Physical | Ethernet (physical) | hardware |
A socket is the end-point for bidirectional
For Internet services using TCP or UDP, your service name is your port number. Important services use well-known port numbers, assigned by the IANA.
// Server code in C
// adapted from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berkeley_sockets
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
struct addrinfo hint;
struct sockaddr_storage bindaddr_storage;
struct sockaddr_in6 *bindaddr6 =
(struct sockaddr_in6 *)&bindaddr_storage;
struct sockaddr_in *bindaddr =
(struct sockaddr_in *)&bindaddr_storage;
struct addrinfo *result;
struct sockaddr_storage peer;
int peersize;
char hbuf[NI_MAXHOST], sbuf[NI_MAXSERV];
int retval;
int i32SocketFD = socket(PF_INET6, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
char msg[] = "Success!\n";
if(-1 == i32SocketFD)
{
perror("can not create socket");
exit(-1);
}
bzero(&bindaddr_storage, sizeof(bindaddr_storage));
bindaddr6->sin6_family = AF_INET6;
bindaddr6->sin6_addr = in6addr_any; /* struct assignment */
bindaddr6->sin6_port = htons(12345);
if(-1 == bind(i32SocketFD,(struct sockaddr*) bindaddr6,
sizeof(struct addrinfo)))
{
printf("error bind failed");
perror("main");
exit(-1);
}
if(-1 == listen(i32SocketFD, 10))
{
printf("error listen failed");
exit(-1);
}
// Here, you should print out your local address using
// getsockname() and getnameinfo() (and gai_strerror on error)
for(; ;)
{
int i32ConnectFD = accept(i32SocketFD, NULL, NULL);
if(0 > i32ConnectFD)
{
// improve error reporting here, using perror()
printf("error accept failed");
exit(-1);
}
// Here, you should print out your local address
// and the peer address using
// getsockname(), getpeername(), and getnameinfo()
// (and gai_strerror on error)
// perform read write operations ...
// add error checking and reporting here
write(i32ConnectFD, msg, sizeof(msg));
// wait one minute; this lets us see the connection in place, and
// even see the behavior as we try to start a second connection
// at the same time
sleep(60);
// add error checking and reporting here
shutdown(i32ConnectFD, 2);
// add error checking and reporting here
close(i32ConnectFD);
}
// add error checking and reporting here
close(i32SocketFD);
return 0;
}
In Linux, as in most Unix systems, the L2

[rdv@localhost Desktop]$ route -v -A inet Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 133.27.56.0 * 255.255.248.0 U 0 0 0 ath1 default gw2-v20.sfc.kei 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 ath1
[rdv@localhost Desktop]$ route -v -A inet6 Kernel IPv6 routing table Destination Next Hop Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 2001:200:1c0:2000::/64 * UA 256 104 0 ath1 fe80::/64 * U 256 0 0 ath1 */0 fe80::213:5fff:fecd:dc00 UGDA 1024 22 0 ath1 localhost6.localdomain6/128 * U 0 1 1 lo 2001:200:1c0:2000:219:7dff:fe0c:f94/128 * U 0 304 1 lo fe80::219:7dff:fe0c:f94/128 * U 0 4 1 lo ff02::1/128 ff02::1 UC 0 6 0 ath1 ff02::1:ff83:8338/128 ff02::1:ff83:8338 UC 0 5 0 ath1 ff00::/8 * U 256 0 0 ath1
A very common security bug is to allow the caller of a
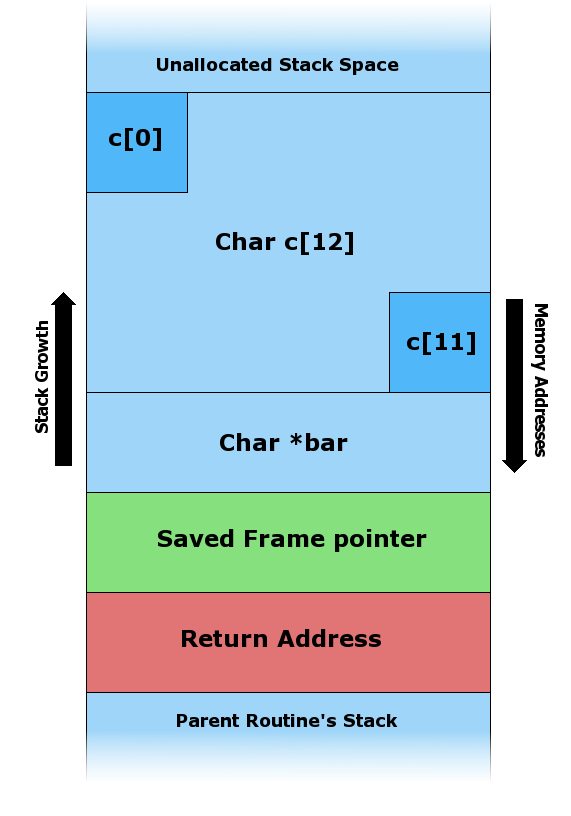 |
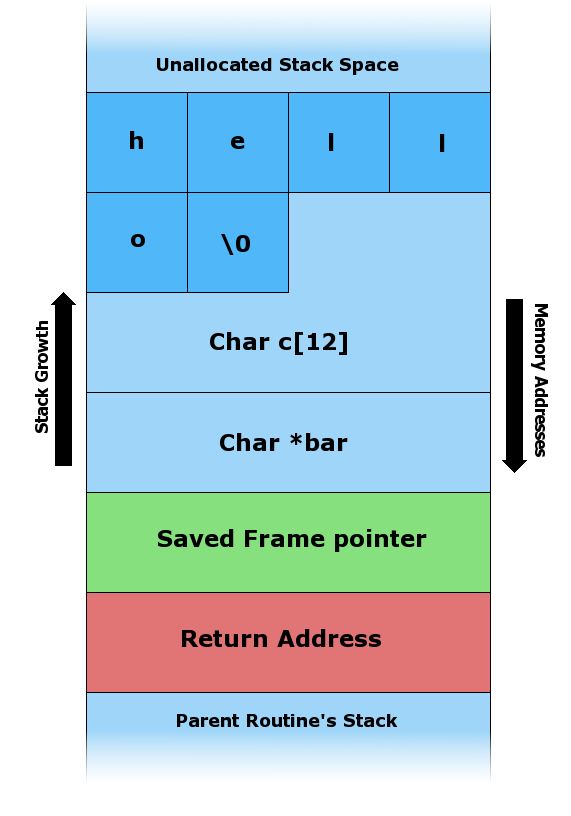 |
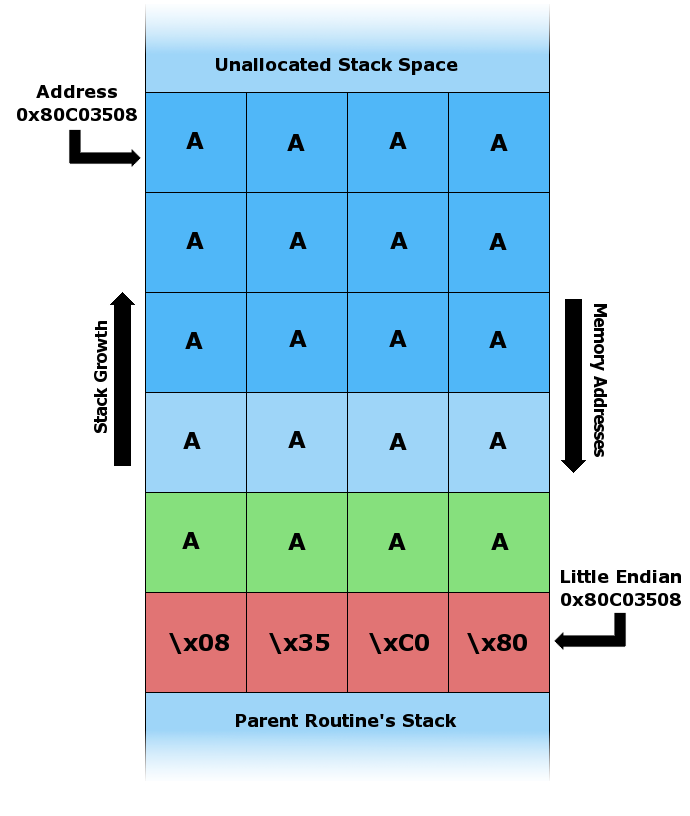 |